Home » Talks (Page 2)
Category Archives: Talks
Philosophy and Poetry in Gorzów Wielkopolski
On May 13th-14th 2024 the Jacob of Paradies Academy in Gorzów Wielkopolski held an international conference Poesis Philosophorum – Philosophia Poetarum. The head, heart and the soul of this symposium was professor Marian Wesoły with whom Oral history team, including AΦR member, had conducted an interview in December 2023, as it was announced here.

Detailed program of the conference can be downloaded here. Tomasz Mróz was one of the speakers on the first day of the conference. In his presentation he took an attempt to demonstrate how Polish poets referred to philosophers, or how philosophers used poetry to explain philosophy.

T. Mróz discussed both ancient and modern philosophers, whose ideas had been referred to by poetic means. Apart from various verses on Copernicus or Jarosław Iwaszkiewicz’s poem on Immanuel Kant, T. Mróz presented Ignacy Krasicki’s (1735-1801) satire on Plato and Stanisław Lisiecki’s (1872-1960) use of a church anthem to explain the predominant character of the Good in Plato’s philosophy.

Krasicki was a leading representative of the Enlightenment literature in Poland. The aim of his poem was to ridicule Plato’s philosophy and the figure of an ancient sage in general: Plato, pompously speaking to his disciples as a possessor of wisdom, is ultimately bitten by a flea who in this way declares its possession over Plato. No philosopher, then, can escape nature!
Lisiecki was not a poet, but over a century later classics scholar and translator of Greek philosophy into Polish. He used the lyrics of a church song, praising inexhaustibility, inexplicability and God’s predominance over the created world. His intention was to demonstrate Polish audience that Plato’s highest Good had a similar character to Christian God, the highest being, and could be easily comprehended by means of analogy.

This paper contributed to the variety of topics discussed during the conference, presenting various relations between philosophy and poetry. The conference in general demonstrated that even smaller academic institutions can gather international participants, organise significant academic events and thus contribute to philosophical life, granted that there is some spiritus movens behind them.
(Another) Erasmus Teaching Visit in Vilnius
In April, 15th-19th, 2024, Tomasz Mróz enjoyed his fourth Erasmus teaching visit in Faculty of Philosophy, Vilnius University.

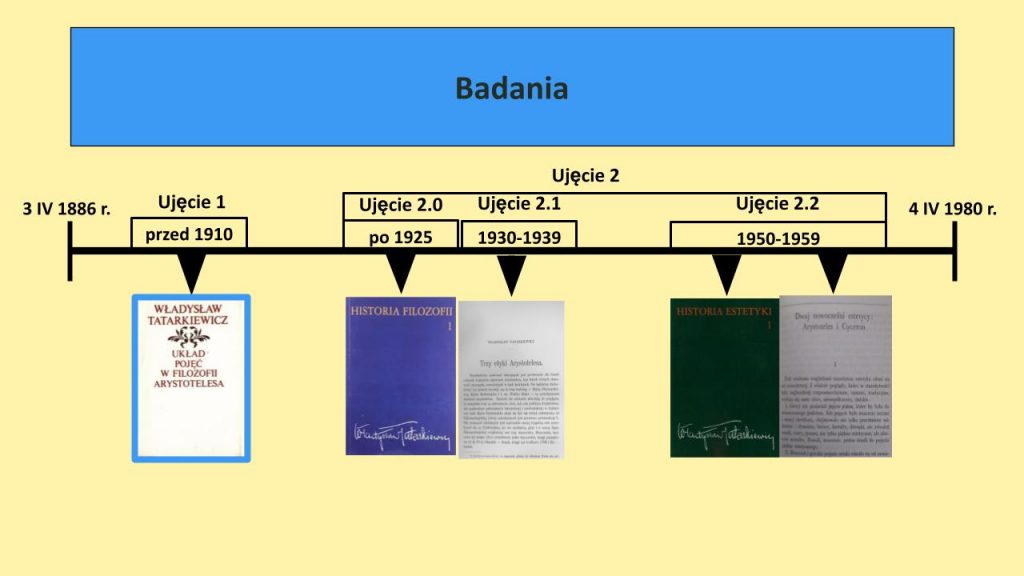
This year, some issues connected to the reception of ancient philosophy were addressed during the lecture on Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980) and his History of Philosophy. It was ancient philosophy as a subject of various problems in historiography of philosophy.

More important, however, was a talk devoted to Vitello (ca. 1230-1300) and his theoretical reflection on the nature of the daemons. Vitello’s demonology stemmed from his research in natural sciences and it employed neo-Platonic and Aristotelian elements, such as a belief in a mathematical structure of the universe, the theory of four elements and natural creatures. Vitello’s philosophical investigations were presented against the background of the 13th century developments in philosophy, especially the Averroist controversy.
Teaching duties were supplemented with meetings with the Faculty members and discussions with students extra universitatis muros. Hopefully, this was not the final chord in the co-operation between Vilnius University and the University of Zielona Góra.
A Visitor from Vilnius and Plato as a Teaching Subject

In March 4th-8th an Erasmus exchange visitor from Vilnius University stayed at the University of Zielona Góra and delivered some talks here. Our guest was dr. Mindaugas Stoškus who is an assistant professor at the Department of Theoretical Philosophy and Philosophy of Science, Faculty of Philosophy, VU.
Among M. Stoškus’ presentations there was one on the methods of teaching ancient philosophy, as a part the reception of ancient philosophy, and it was delivered to the students in the Doctoral School of Humanities and Social Sciences and to invited guests. The central topic of his lecture was Plato’s Republic and Plato’s political project which, resulting from Stoškus’ interactive co-operation with the audience, turned out to be a tricky and problematic issue. The lecturer demonstrated to the audience, consisting mostly of non-philosophers, how superficial reading of Plato’s opus magnum may lead to misunderstanding of the true nature of his political aims, one of which was disjoining wealth and personal success from political power and responsibility.
We hope that M. Stoškus’ visit at UZ is not the final chord of the co-operation between our two partner institutions and that our mutual collaboration will develop.
AΦR at the Twelfth Polish Congress of Philosophy in Łódź
In September (11th-16th) 2023 the 12th Polish Congress of Philosophy took place in Łódź. Three members of AΦR took part in this great event, and they delivered four papers there. Tomasz Mróz spoke about three traditions of doing philosophy and three interpretations of Plato at the ancient philosophy section, and the other three papers were presented in the section of Polish philosophy: on the influence of Aristotle on the works of W. Tatarkiewicz (Adrian Habura); on H. Jakubanis’ arguments for the reneval of philosophy in accordance to its ancient roots (Mariam Sargsyan); and on B. Kieszkowski, a researcher of Renaissance Platonism, on his life, works and their reception (again T. Mróz).

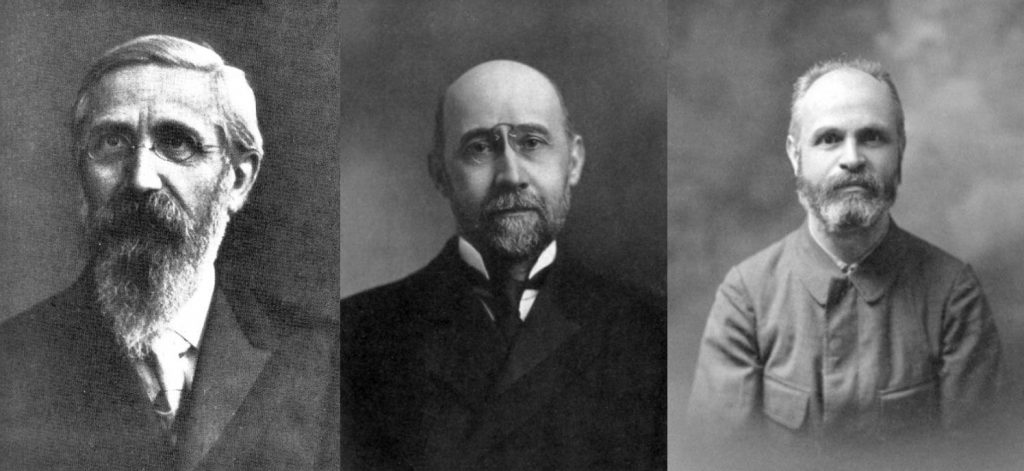
T. Mróz’s paper, Three Traditions of Doing Philosophy and Three Interpretations of Plato, was devoted to presenting three Plato scholars of the turn of the 20th century, Paul Natorp (1854–1924), a German, Paul Shorey (1857–1934), an American, and Wincenty Lutosławski (1863–1954), a Pole, and their interpretations of Plato. Mróz attempted to relate these three personalities of one generation and their Platonic studies with their native, dominant philosophical traditions: neo-Kantianism, Emersonian tradition and Polish Romantic Messianism. Their methodologies, views on the chronology of the dialogues and the status of ideas were discussed, as a starting point for future comparative research of their Platonic studies and reciprocal references.

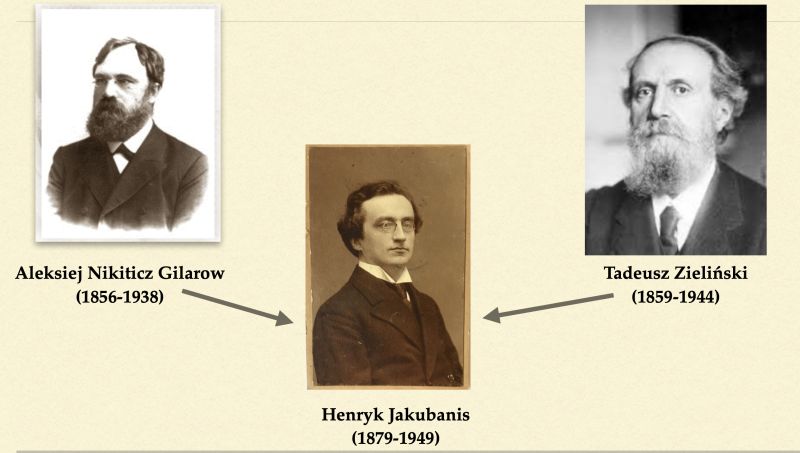
M. Sargsyan’s presentation was titled: Arguments of Henryk Jakubanis (1879-1949) for Renewal of Philosophy and Culture on the Ancient Model. It started with an introductory part about the biography of Jakubanis to familiarise the audience with his personality. Then the main part followed and it consisted in discussing Jakubanis’ work The Significance of Ancient Philosophy for the Modern View of the World (1910). Historical and philosophical research methods of Jakubanis were analysed and compared with those of his academic supervisor in Kyiv, Alexei Gilarov. Another comparative perspective was provided by the works of Tadeusz Zielinski, who was an internationally recognised scholar, and a kind, older colleague for Jakubanis.
A. Habura’s paper was titled Aristotle in the Works of Władysław Tatarkiewicz and divided into two parts. In the first one, following Tatarkiewicz’s own statement, Habura distinguished two “images” of Aristotle’s philosophy which Tatarkiewicz had developed during his research career. Habura took into account various works of Tatarkiewicz and demonstrated that these two images were not contradictory, but rather complementary to each other. In the second part of his presentation Habura distinguished five aspects of Aristotle’s inspiration in Tatarkiewicz’s works, in accordance with Tatarkiewicz’s own reflection on this topic, and proved a significant, substantial and lasting impact of Aristotle on Tatarkiewicz’s original philosophical investigations.
Second paper by Mróz was a presentation of a further development of his research on Bohdan Kieszkowski, a Polish scholar who was a specialist on Renaissance Platonism and Pico della Mirandola. Earlier this year Mróz discussed Kieszkowski’s biography, but this time the focus was on Kieszkowski’s works and their reception, that is, his polemic with another Polish expert in Renaissance philosophy, M. Heitzman (1899-1964), on the sources of Renaissance Italian Platonism, and a critical reception of Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico’s Conclusiones (1973) by a Portuguese researcher, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010). Heitzman searched for the roots of philosophy in Florentine Academy in medieval thought, while Kieszkowski tended to emphasise the role of ancient sources. As for Pina Martins, he praised Kieszkowski’s erudition, yet pointed to a large number of errors in Conclusiones, resulting from various reasons, including Kieszkowski’s lack of precision in reading Latin texts.

Bertrand Russell, His Views on Ancient Philosophy and Critical Reaction on Them in Poland
In August 17-18th T. Mróz took part in the sixth annual History of Analytic Philosophy Workshop organised by Tilburg Center for Moral Philosophy, Epistemology and
Philosophy of Science. This year’s meeting was devoted to Global Reception of Russell’s Scientific Philosophy.

T. Mróz’s paper was prepared in co-operation with Paweł Polak (The Pontifical University of John Paul II in Kraków), who presented his part in an on-line form. The title of their presentation was The Early Reception of Russell’s Philosophy among Polish Philosophers – a Diversity of Perspectives. P. Polak focused in particular on reception of Russell’s ideas among the representatives of the Lvov-Warsaw School, while T. Mróz discussed two cases of reception of Russell’s History of Western Philosophy (1945) among Polish historians of philosophy, and some other issues, e.g. the censorship of Russell’s texts in Poland.

What matters here is ancient philosophy. The first Polish critic of Russell’s History was Wincenty Lutosławski (1863-1954), who expressed his views on Russell’s Plato in a letter (Lutosławski’s draft on the left) to the author (a paper in “Russell” on the letters between the two philosophers has been announced here). Despite the differences between them, Lutosławski declared in his letter: “Your History proves that we agree in our esteem of Plato”. Moreover, he praised Russell, “In your six chapters on him [=Plato] I did not discover a single error and I agree with everything you say”. In fact, both authors set themselves different goals in discussing Plato and this resulted in disparate methods in their presentations of Platonism, yet Lutosławski’s opinion was so important for Russell that he passed it immediately to his publisher.
Marian Heitzman (1899-1964) was not a philosopher of a similar recognition to Lutosławski, he was an expert in Renaissance philosophy and in F. Bacon. His views on Russell’s History were published as an extensive review study in the oldest Polish philosophical journal „Philosophical Review” [Przegląd Filozoficzny]. His general opinion on Russell’s book was the following: “it is worth to read the book and it is worth to have it on a bookshelf, but it cannot be recommended as a handbook or a synthetic study of the history of philosophy”. He appreciated Russell’s style and his „humour coloured by a bit of Volterian scepticism”. His focus was Renaissance philosophy, but he remarked on many deficiences in Russell’s chapters on ancient topics. For example, the missing or too shortly discussed subjects, according to Heitzman, included Gorgias, Zeno and the logic of the Stoics. Although Russell intended to emphasise issues in political and social philosophies, in Heitzman’s eyes he missed the cosmopolitanism of the Cynics and misrepresented the problem of the Sophists and democracy. Finally, Russell aimed to present various philosophers as the effects of their social conditions, but he failed to illustrate this with Antisthenes of Athens (not an Athenian citizen) and his philosophy of cynicism.

20th Annual Conference of the International Society for Neoplatonic Studies
International Society for Neoplatonic Studies (ISNS) has for decades been a forum for scholars researching various phaenomena in the history of Neoplatonism, including even the latest developments of the reception of Platonism. In June 14th-17th, 2023, ISNS conference was held at the foot of Etna, in Catania, in co-operation with Università degli Studi di Catania.
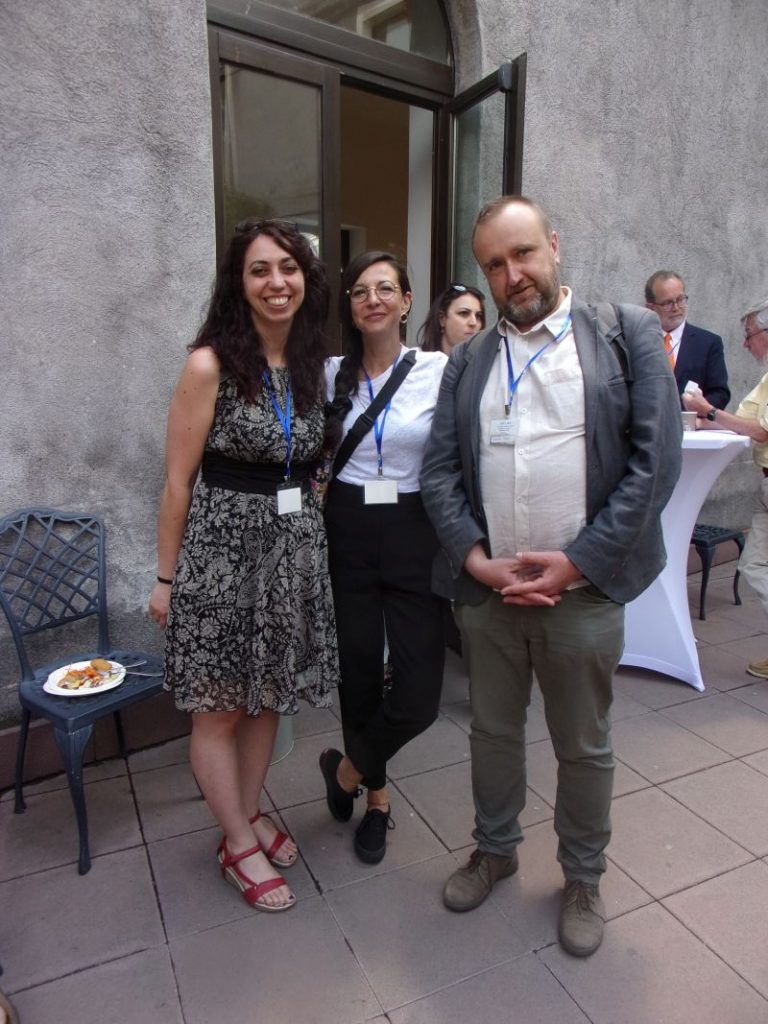


One of the numerous panels at the conference was devoted to Plato’s Timaeus, the concept of time and its influence on various thinkers across the history of philosophy up to recent times. The panel was organised by the two professors, Laura Marongiu and Laura Follesa, both of University of Milan. Although this panel focused on relatively narrow topic, the response from scholars was impressive and thus the list of speakers in this successful panel demonstrated incessant interest of generations of scholars in the Timaeus, the late dialogue of Plato. The topics ranged from Speusippus, Aristotle, Xenocrates, Numenius, Plotinus, Iamblichus, Proclus, Simplicius and Philoponus to M. Ficino, L. Bruno, F.W.J. Schelling, G.W.F. Hegel, H. Bergson and E. Husserl (on the photo: L. Follesa, L. Marongiu & T. Mróz).
T. Mróz presented a paper titled The Timaeus and Three Scholars of One Generation: P. Natorp, P. Shorey and W. Lutosławski. Mróz discussed various interpretations of the Timaeus by the three scholars, focusing on their general methods in reading Plato and their views on Plato’s concept of the time, although none of them considered the time to be the central issue in the dialogue.

ISNS conferences have always been a forum for scholars who explore various aspects of Platonism, Neoplatonism and Plato reception from antiquity up to contemporary times. Professor John Finamore, spiritus movens of all of ISNS symposia, spares no efforts to hold ISNS events in various academic centres and to provide opportunity for scholars throughout the world to take part in them. He has recently announced that next year’s ISNS conference will take place in Dublin, in co-operation with Trinity College.
AΦR at the 11th Seminar of the Historians of Polish Philosophy in Częstochowa
Seminar of the Historians of Polish Philosophy is a cyclic academic meeting which gathers philosophers and historians of philosophy who focus on the history of philosophy in Poland. 11th edition of this seminar was held in Częstochowa at Philosophy Department of Jan Długosz University on May 15th-16th, 2023, and it was focused, not surprisingly, on the topics of war and peace.

Two AΦR members delivered their papers there. Adrian Habura’s paper was not directly devoted to the reception of ancient philosophy, for he focused on the first edition of Władysław Tatarkiewicz’s (1886-1980) work O szczęściu [Analysis of Happiness] (1947), and took an attempt to analyse the content of the book and search for the topics related to war issues to determine possible origin of each chapter, that is, to divide the chapers into two groups: those composed by Tatarkiewicz before the outbreak of the World War II and those compose after it.
Tomasz Mróz, in turn, presented a largely unknown biography of a 20th century Polish researcher of Florentine neo-Platonism. His presentation had a long title: Bohdan Kieszkowski (1904-1997): a Researcher of Renaissance neo-Platonism and His Career Destroyed by the War (with the materials collected by Professor Czesław Głombik).
Kieszkowski published his works in Polish, Italian and French, and edited Conclusiones by Giovanni Pico della Mirandola (Geneve 1973). His opus vitae was the book Platonizm renesansowy [Renaissance Platonism] (Warszawa 1935), subsequently published in Italian as Studi sul platonismo del rinascimento in Italia (Firenze 1936). His studies were discussed mostly in Poland, Italy, France and Spain, but existing sources allowed only to reconstruct his biography to the first years after the World War II.


Materials collected by prof. C. Głombik (1935-2022) from family archives shed some light on Kieszkowski’s life on an exile in France. He was meeting there his former supervisor from the University of Warsaw, W. Tatarkiewicz, who was able to visit Paris several times in the sixties and considered Kieszkowski to be his best student. The letters from Tatarkiewicz to Kieszkowski’s sister, Wanda, reveal the facts concerning the details of a difficult life of a scholar on the exile. To Tatarkiewicz’s disappointed Kieszkowski was considering a turn in his focus from Renaissance studies to military history, yet he was very compassionate about his former student because he was aware of Kieszkowski’s physical and psychological limitations, resulting from his war and after war experiences. His legs, for example, were severely injured by German air raids already in 1939, he narrowly avoided amputation and throughout his life he experienced the negative effects of this until the end of his life. Communication between Tatarkiewicz and Kieszkowski was also affected by the fact that the former’s hearing was impaired and the latter spoke very quietly, as if he was afraid that someone could overhear them. Nevertheless, Kieszkowski’s works on Renaissance Platonism won recognition in the academic world and it is an interesting task to research their reception and impact.

Recent commentaries