Home » Posts tagged 'R. W. Emerson'
Tag Archives: R. W. Emerson
American Platonism and ISNS Dublin Conference
International Society for Neoplatonic Studies, in accordance with its name, promotes studies and academic work on Platonism, Neoplatonism and Platonic tradition broadly considered. In co-operation with various academic centres throughout the world ISNS organises annual conferences with large number of panels covering a wide spectrum of what can be called Neoplatonism. In 2024 the conference was held in Trinity College, Dublin on June 19th-23rd.

Among numerous panels of the Dublin conference there was one on the American Platonic tradition, its title was: Transcendental Echoes: Neoplatonism’s Influence on American Renaissance Thought. The aim of this panel was described by its originator, prof. Sonya Isaak, as follows: “this interdisciplinary panel endeavors to explore the dynamic intersections between Neoplatonism and American Transcendentalism, elucidating the profound philosophical, spiritual, and literary amalgamations that defined this vibrant movement in the 19th century…”. The panel had only three speakers (prof. Jay Bregman, prof. S. Isaak and T. Mróz), but it gathered many participants in the audience who wanted to learn bout the developments of Platonism in the 19th century American thought.
T. Mróz’s paper was titled Paul Shorey as a Plato Scholar and his Influences from Ralph Waldo Emerson. Shorey (1857–1934) was the most eminent and internationally recognised American Plato scholar at the turn of the 20th century. He took part in the then international disputes on interpreting Plato’s philosophy and the very methods of reading and researching the dialogues.

As an American Plato scholar, Shorey, in his works on Plato, did not avoid referring to American writers, with a particular emphasis on Emerson (1803–1882), the author of Representative Men (with a significant essay on Plato). Shorey, naturally, included Emerson in a long line of thinkers inspired by Plato, but the aim of Mróz’s paper was to focus on the influence exerted by the Transcendentalist writer and philosopher, Emerson, on the classics scholar and academic researcher, Shorey. Although he did not hold Emerson as a philosopher in high regard, there are some traits of his thinking of Plato which may be ascribed with Emersonian origins, for example, reading Plato as a moral philosopher and tendency toward unity. Thus the connection between American Transcendentalist movement and academic studies on Plato in American tradition was demonstrated.
AΦR at the Twelfth Polish Congress of Philosophy in Łódź
In September (11th-16th) 2023 the 12th Polish Congress of Philosophy took place in Łódź. Three members of AΦR took part in this great event, and they delivered four papers there. Tomasz Mróz spoke about three traditions of doing philosophy and three interpretations of Plato at the ancient philosophy section, and the other three papers were presented in the section of Polish philosophy: on the influence of Aristotle on the works of W. Tatarkiewicz (Adrian Habura); on H. Jakubanis’ arguments for the reneval of philosophy in accordance to its ancient roots (Mariam Sargsyan); and on B. Kieszkowski, a researcher of Renaissance Platonism, on his life, works and their reception (again T. Mróz).

T. Mróz’s paper, Three Traditions of Doing Philosophy and Three Interpretations of Plato, was devoted to presenting three Plato scholars of the turn of the 20th century, Paul Natorp (1854–1924), a German, Paul Shorey (1857–1934), an American, and Wincenty Lutosławski (1863–1954), a Pole, and their interpretations of Plato. Mróz attempted to relate these three personalities of one generation and their Platonic studies with their native, dominant philosophical traditions: neo-Kantianism, Emersonian tradition and Polish Romantic Messianism. Their methodologies, views on the chronology of the dialogues and the status of ideas were discussed, as a starting point for future comparative research of their Platonic studies and reciprocal references.

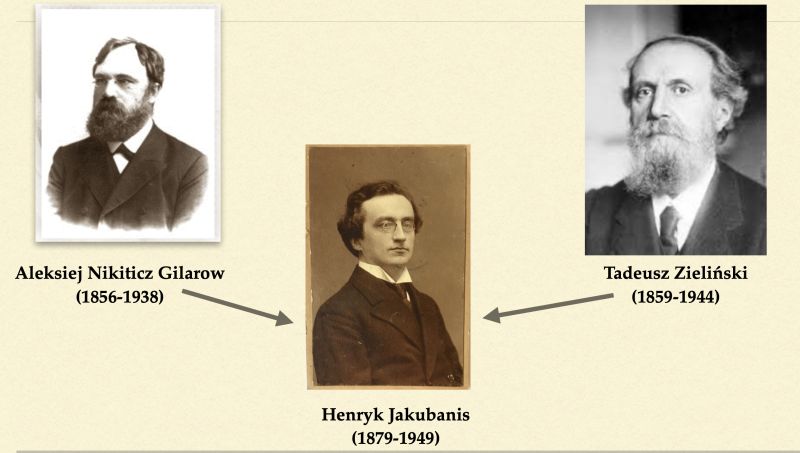
M. Sargsyan’s presentation was titled: Arguments of Henryk Jakubanis (1879-1949) for Renewal of Philosophy and Culture on the Ancient Model. It started with an introductory part about the biography of Jakubanis to familiarise the audience with his personality. Then the main part followed and it consisted in discussing Jakubanis’ work The Significance of Ancient Philosophy for the Modern View of the World (1910). Historical and philosophical research methods of Jakubanis were analysed and compared with those of his academic supervisor in Kyiv, Alexei Gilarov. Another comparative perspective was provided by the works of Tadeusz Zielinski, who was an internationally recognised scholar, and a kind, older colleague for Jakubanis.
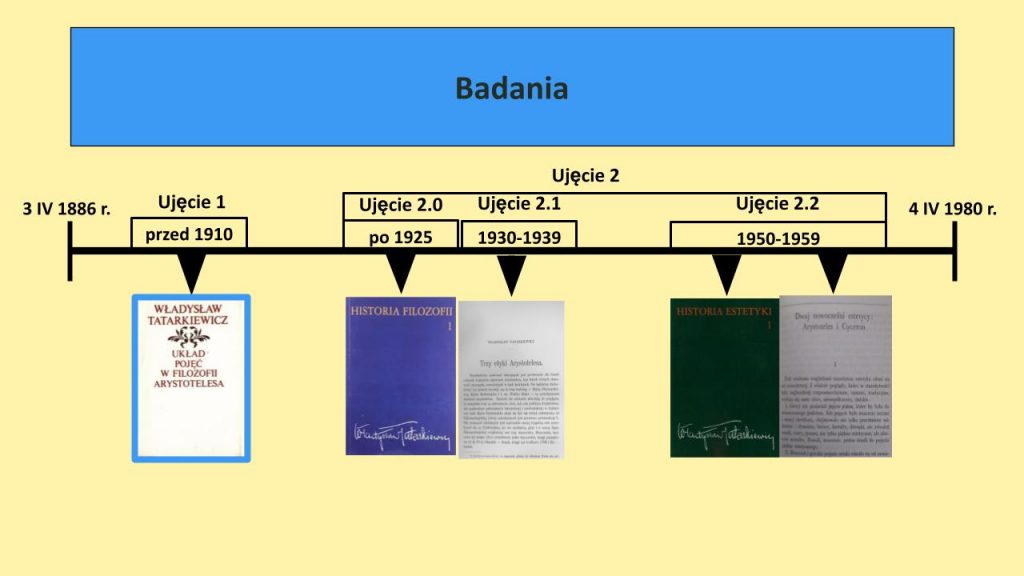
A. Habura’s paper was titled Aristotle in the Works of Władysław Tatarkiewicz and divided into two parts. In the first one, following Tatarkiewicz’s own statement, Habura distinguished two “images” of Aristotle’s philosophy which Tatarkiewicz had developed during his research career. Habura took into account various works of Tatarkiewicz and demonstrated that these two images were not contradictory, but rather complementary to each other. In the second part of his presentation Habura distinguished five aspects of Aristotle’s inspiration in Tatarkiewicz’s works, in accordance with Tatarkiewicz’s own reflection on this topic, and proved a significant, substantial and lasting impact of Aristotle on Tatarkiewicz’s original philosophical investigations.
Second paper by Mróz was a presentation of a further development of his research on Bohdan Kieszkowski, a Polish scholar who was a specialist on Renaissance Platonism and Pico della Mirandola. Earlier this year Mróz discussed Kieszkowski’s biography, but this time the focus was on Kieszkowski’s works and their reception, that is, his polemic with another Polish expert in Renaissance philosophy, M. Heitzman (1899-1964), on the sources of Renaissance Italian Platonism, and a critical reception of Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico’s Conclusiones (1973) by a Portuguese researcher, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010). Heitzman searched for the roots of philosophy in Florentine Academy in medieval thought, while Kieszkowski tended to emphasise the role of ancient sources. As for Pina Martins, he praised Kieszkowski’s erudition, yet pointed to a large number of errors in Conclusiones, resulting from various reasons, including Kieszkowski’s lack of precision in reading Latin texts.

Recent commentaries